
CHAPTER-13 || OUR ENVIRONMENT ||
TABLE OF CONTENT :-
1•1- What happens when we put our waste into the environment?
1•2- What is the ecosystem and its components?
1•3- How do our activities affect the environment?
|| INTRODUCTION ||
Environment:- It is a set of physical, chemical and biological elements surrounding an organism which affects it.
Components of Environment:
(1)-Physical components : – Air, water, soil, temperature, sunlight.
(2)-Chemical components:- Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, etc.
(3)-Biotic components:- Plants, animals, microorganisms, etc.
The digestion of the food we eat is done by various enzymes. Enzymes are specific in their action. A specific enzyme is required for the digestion of a particular type of substance.
|| 1•1 || TOPIC NO.1 || What happens when we throw our waste into the environment? ||
Enzymes:-Enzymes are a type of protein that speed up chemical reactions in the body. Enzymes are also called “biological catalysts”.
We get energy by eating food, but we cannot get energy by eating coal. This is the reason why many man-made substances like plastic cannot be decomposed by bacteria. These substances are affected by physical conditions such as heat and pressure but they remain in the environment for a long time under normal conditions.
Biodegradable substances:- Substances that are degraded through biological processes. Such as fruit peels, leaves etc.
Non-biodegradable substances:- Substances that do not decompose through biological processes. Such as plastic etc.
|| 1•2 || TOPIC NO.2 || Ecosystem What are its components?
Ecosystem:- All the organisms of an area and the abiotic factors of the environment together form an ecosystem. Therefore, an ecosystem has the biotic components and abiotic components of all the organisms.
Ecosystem = Biotic Components + Abiotic Components
Types of ecosystem: –
(1)-Artificial or man-made ecosystem- This includes gardens, farms etc.
(2)-Natural Ecosystem- This includes forests, ponds and lakes etc.
Physical factors include abiotic components such as temperature, rainfall, air, soil and minerals etc.
On the basis of survival, organisms are divided into producers, consumers and decomposers.
Producers:- All green plants, blue-green algae which have the ability to photosynthesize come under the producer category. Autotrophs absorb the energy contained in light and convert it into chemical energy.
Consumers:- All organisms directly or indirectly depend on producers for their survival. These organisms which directly or indirectly depend on the food produced by the producers come under the consumer category. Consumers are divided into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites.
Decomposers/Decomposers:- Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi decompose dead remains. These microorganisms are decomposers because they convert complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances, which go into the soil and are reused by the plants.
Organic matter :- The substance which contains carbon is called organic matter.
Inorganic matter :- The substance which does not contain carbon is called organic matter.
(2.2.1)- Food Chain:- It is the sequence of transfer of food and energy between organisms in an ecosystem. It shows that one organism obtains energy by eating another organism.
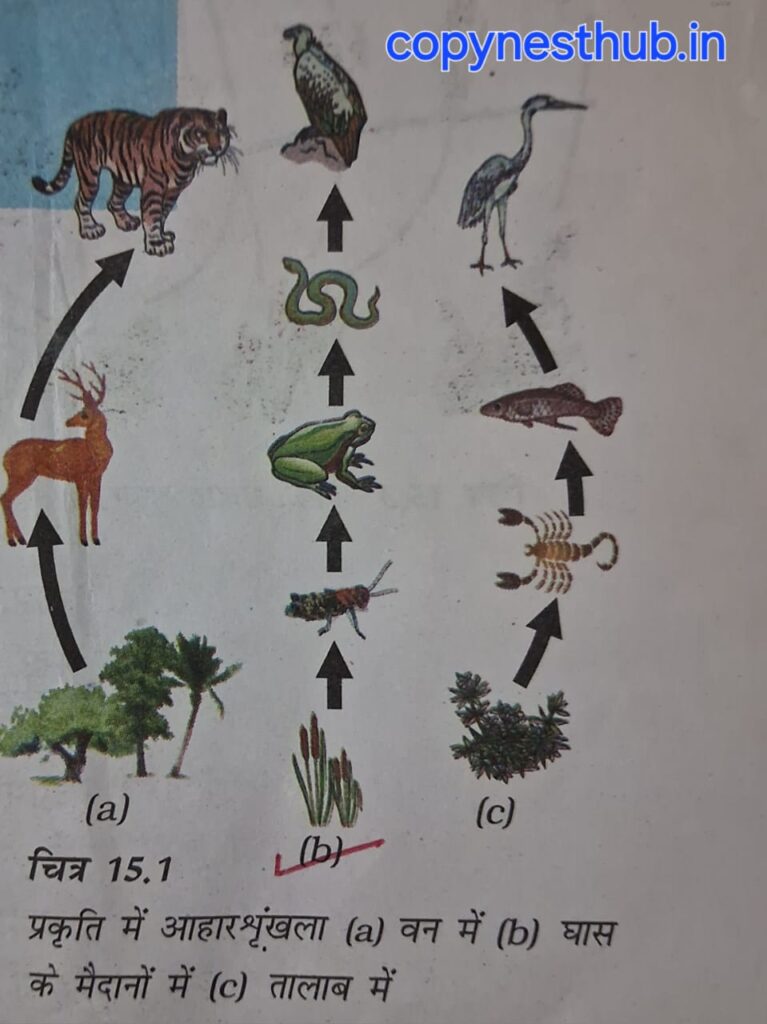

Producer- first trophic level.
Herbivores or primary consumers- second trophic level.
Secondary consumers- third trophic level.
Tertiary consumers- fourth trophic level.
Each step of a food chain forms a trophic level.
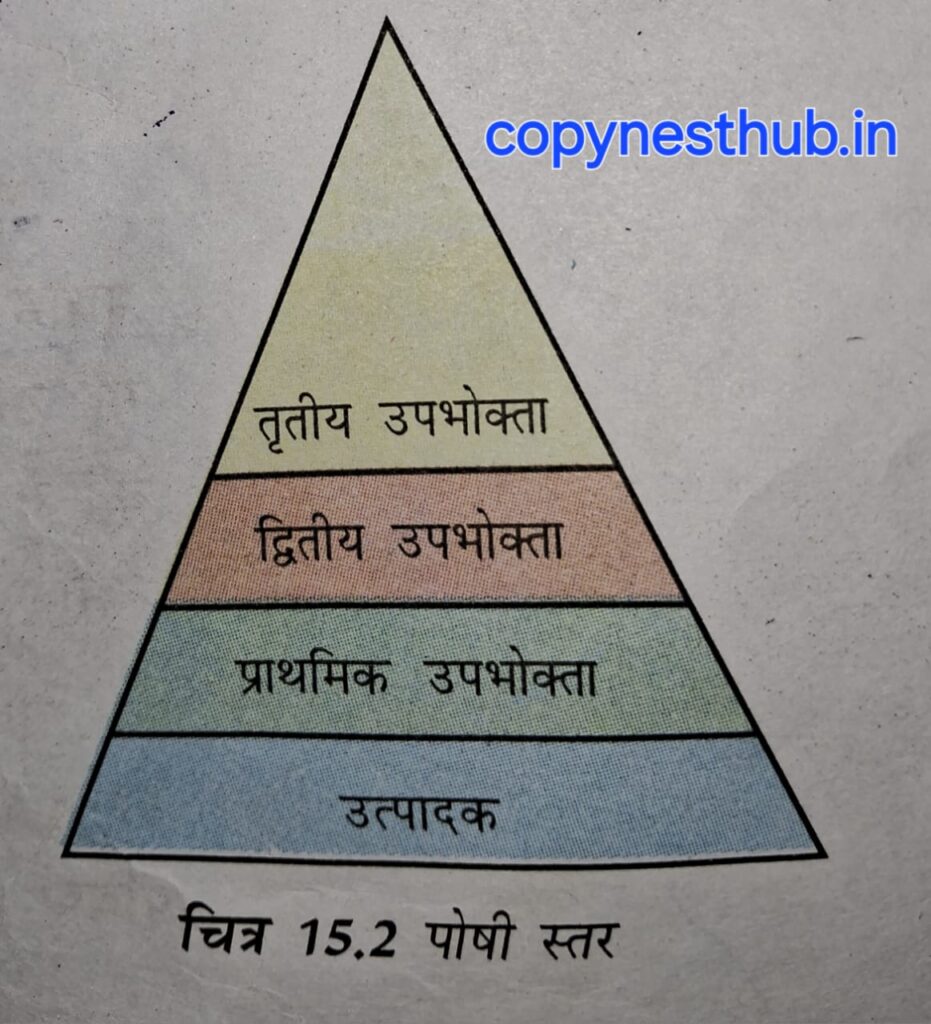
Rule of 10 Percent:- also known as Lindemann’s 10% rule, states that only 10% of the energy in an ecosystem is transferred from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level .
NOTE:- Generally the number of organisms is more at the lower trophic level. Hence this number is the highest at the producer level.
(2.2.1)- Food web:- A food web links several food chains, creating multiple pathways for the flow of energy.
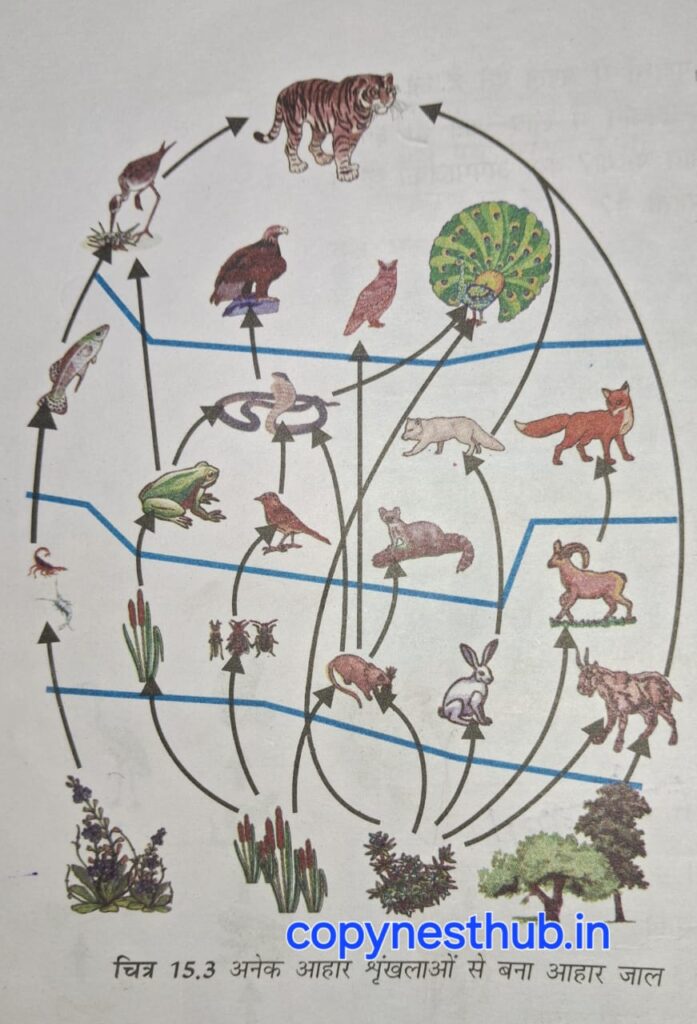
NOTE :- Energy – The capacity to do work is called energy.
There is transformation of energy from one form to another.
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It can only be converted from one form to another.
The flow of energy occurs in one direction only.
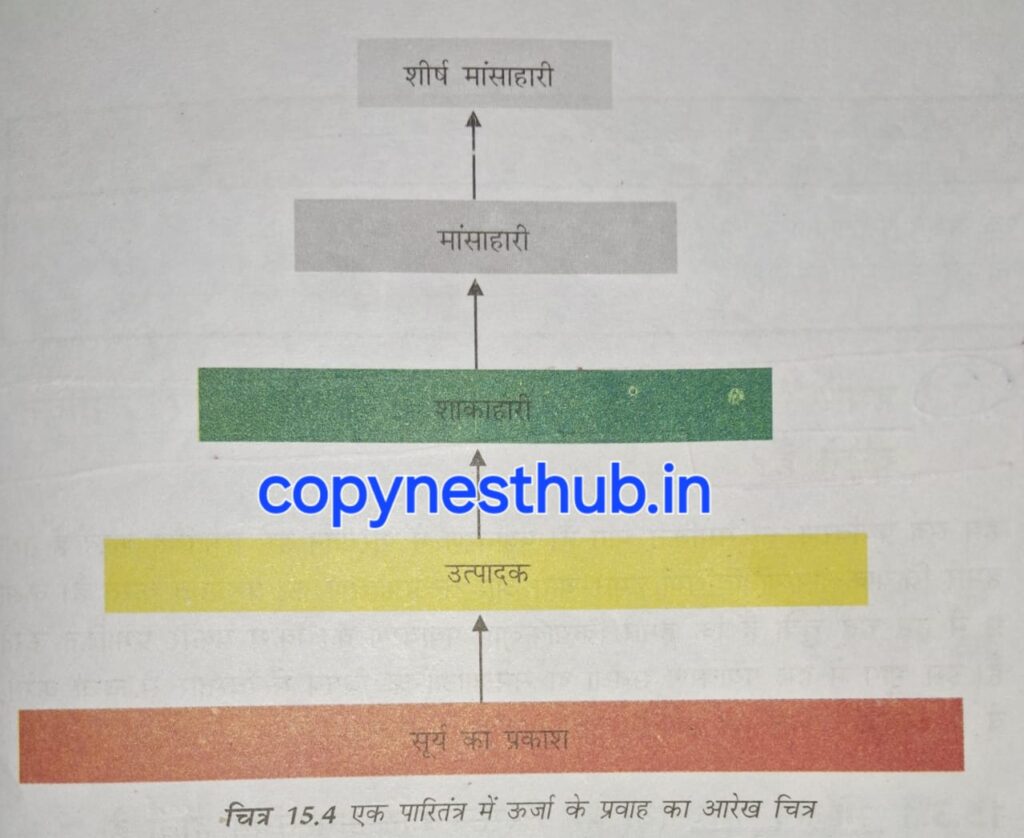
Sunlight 》 Producer 》 Herbivores 》 Carnivores 》 Top Carnivores
|| 1•3 || TOPIC NO.3 || How do our activities affect the environment?
Ozone Layer:- Ozone molecules are made up of three atoms of oxygen.
Ozone gas is found in the stratosphere (second layer of the atmosphere).
(2.3.1)- What is the ozone layer and how does it degrade?- At higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone is formed from oxygen molecules due to the effect of ultraviolet radiation (UV). High energy ultraviolet radiation disintegrates oxygen molecules to form free oxygen atoms. These free oxygen atoms combine to form ozone.
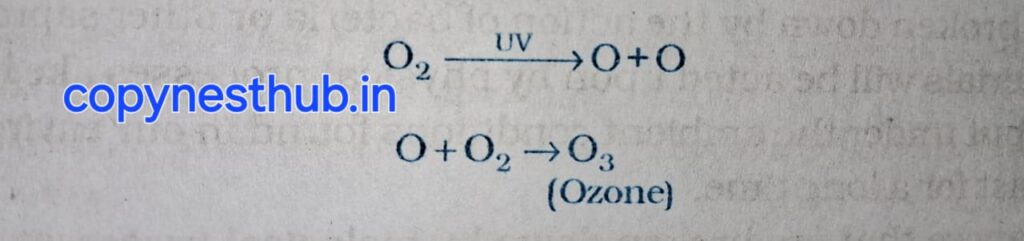
Importance of Ozone:- Ozone layer in the stratosphere:- This layer protects the Earth by absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation coming from the Sun.
Ozone in the Troposphere:- It is a pollutant that causes air pollution, especially in urban areas, and is considered a major component of “smog”.
Since 1980 , the amount of ozone in the atmosphere started declining rapidly.
CFC(Chlorofluorocarbons):- CFC stands for Chlorofluorocarbons. It is a group of organic compounds that contain carbon, chlorine and fluorine atoms.
CFCs were used as refrigerants (cooling), fire fighting. However, CFCs are known to damage the ozone layer, so their use has now decreased and they have been banned in many countries.
In 1987, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reached a consensus that CFC production should be limited to 1986 levels.
(2.3.2)- Waste Management:- A process that involves collecting, transporting, processing and safely disposing of waste.
Its main objective is to reduce the harmful effects of waste on the environment and human health, as well as to conserve resources and promote sustainable development.
THANKS FOR READING…